 This post is for parents concerned about their child’s reading; for news and social media junkies who want to intelligently respond to current events, such as the recent dramatic improvement in Mississippi reading scores due, largely, to a re-emphasis on phonics; for elementary teachers who never had a phonics course in their teaching credential program; for secondary teachers who wonder, “Should I be teaching phonics to my frosh English students who can barely read?”; and for literacy coaches and reading specialists, like me, who want a quick start user guide to present to parents and teachers. In this 10-minute read, you’ll find out what the following terms mean and what they have to do with teaching phonics, enough to keep you from sounding stupid in any job interview or lunch conversation with other parents, principals, teachers, language coaches, and reading specialists.
This post is for parents concerned about their child’s reading; for news and social media junkies who want to intelligently respond to current events, such as the recent dramatic improvement in Mississippi reading scores due, largely, to a re-emphasis on phonics; for elementary teachers who never had a phonics course in their teaching credential program; for secondary teachers who wonder, “Should I be teaching phonics to my frosh English students who can barely read?”; and for literacy coaches and reading specialists, like me, who want a quick start user guide to present to parents and teachers. In this 10-minute read, you’ll find out what the following terms mean and what they have to do with teaching phonics, enough to keep you from sounding stupid in any job interview or lunch conversation with other parents, principals, teachers, language coaches, and reading specialists.
Think of this as a Quick Start User Guide to Phonics. In order of appearance: phonics, phonemes, graphemes, decoding, encoding, synthetic phonics, explicit and systematic phonics, sound-spellings, decodables, sound-by-sound blending, slanted /lines/, consonant blends, consonant digraphs, analytic phonics, onsets, rimes, word families, diphthongs, embedded phonics, implicit and incidental instruction, cueing systems, MSV, guided reading, r-controlled vowels, silent final e, instructional phonics sequence, continuous sounds
Definitions
Let’s begin by defining phonics. Simply put, phonics is how we use the 26 letters of the alphabet as a code to represent our English phonemes (the fancy way of saying the 43 or 44 speech sounds). We put together these written speech sounds (called graphemes if you want to sound impressive) to read words. This is known as decoding. The Latin prefix, “de” means away from or out of, which helps us remember that decoding is making meaning out of the letter combinations. The other side of the language coin from decoding is encoding. The Latin prefix, “en” means in or into, which helps us remember that encoding is making the graphemes into words. To keep it simple: Decoding is sounding-out the words to be able to read them, and encoding is spelling the words.
Now that we have a definition of phonics, let’s take a look at the three approaches to phonics instruction. In our brief analysis, you’ll learn the key components of phonics instruction in the key instructional activities and the methods used by each phonics approach to teach them. To be clear, each approach helps students learn the phonics rules; it’s the how they are learned that differs. As an aside, these three methods of teaching phonics are the main points of contention in the never-ending Reading Wars, and the battles within each approach are just as contentious as those among the three approaches.
Types of Phonics Approaches

Animal Sound-Spelling Cards
1. Synthetic Phonics: In this approach, teachers help students learn how to convert the 26 letters of the alphabet into the 43 or 44 English phonemes (speech sounds) and then blend these individual sounds to read words. The teacher introduces the graphemes (the spellings) for each of these phonemes in explicit, systematic instruction. Explicit means direct and sometimes isolated instruction that is unconnected to text. Systematic means planned, structured, and sequenced instruction.
Key Instructional Activities: The sound-spelling card (to the right) is a key instructional component of synthetic phonics. For example, students first learn the sounds and spellings listed on the three cards. (Previously, students had learned the /s/ on the seagull card and the /n/ on the newt card before the teacher introduces the sn_ on the snack card.)
Another key instructional activity is sound-by-sound blending. The teacher asks students to say the consonant blend sounds on the snack card; say the vowel sound on the iguana card; say the consonant digraph sound on the cheetah card; and then blend the word, snitch. Students are taught the phonics rule that the _tch spelling follows short vowel sounds.
A third synthetic activity is the use of decodables. Decodables are short books, designed to practice specific sound-spellings introduced in the sound-by-sound blending activities. Decodables also review previously learned sound-spellings. Typically, a limited number of non-decodable sight words are used so that students build confidence in using their phonics skills.
*Note: The slanted /lines/ indicate sounds. The _blanks_ indicate that other letters must come before and/or after the spelling. A consonant blend is two or three consonants that frequently appear together at the start or end of syllables. A vowel, most commonly a, e, i, o, and u, appears in every syllable. A consonant digraph is two consonants which form one sound.
Word Families
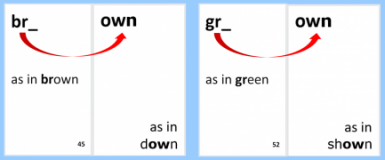
2. Analytic (Analogy) Phonics: Teaches students to look at the whole word, especially the onset (the beginning letter or letters) and rime (the sound pattern known as a word family), and to compare to similarly structured words which are already known.
Key Instructional Activities: For example, the teacher might teach the consonant blends br, cr, dr, and fr as onsets and the rime, own (rhymes with down). Students practice combining the onsets and rimes as br-own, cr-own, dr-own, and fr-own. In the next lesson the teacher might teach the consonant blends gr, thr, and the consonant digraph sh as onsets and the rime, own (rhymes with phone).
Analytic phonics may include explicit and systematic instruction. Teachers introduce the rimes (word families) by syllable types.
*Note: The “ow” spelling in “own” as in brown is a diphthong. A diphthong is a vowel team in which two sounds are made. However, the the “ow” spelling in “own” as in shown is a vowel digraph. A vowel digraph is a vowel team in which only one sound is made.
3. Embedded Phonics: Teaches students phonics within the context of reading as needed to cue the pronunciation of a word. In contrast to the explicit and systematic instruction of the synthetic and analytic approaches, embedded phonics utilizes an implicit, incidental methodology. Phonics skills are learned deductively from the whole to the part as one of the three cueing systems for comprehension i.e., 1. M = Meaning 2. S = Structure (sentence structure, grammar, word order) 3. V = Visual (phonics, onsets and rimes, sight words).
Key Instructional Activities: The teacher groups readers by reading levels and students chorally and individually read a book together. When students struggle with the pronunciation of a word, they apply specific strategies to logically guess the pronunciation. For example, “What’s the sound of the first letter in this word? What word would make sense withe other words in the sentence? What hint does the picture on the page provide as to how to say it?”

The r-Controlled Vowels
A typical embedded phonics lesson might be planned as a mini lesson from a guided reading lesson on a book which uses a number of r-controlled vowels. After an initial reading, the teacher might ask students to search for and create a sorted list for all words using the /ar/, /or/, and /er/ spellings found on the cards to the right. Often, teachers use running records assessments of oral readings to determine the content of the mini lessons.

Silent Final e
Teachers may share the silent final e rule in which the final e at the end of a syllable makes the preceding vowel say its name (a long vowel sound) when a single consonant is found between the vowel and the final silent final e. For example, using the cards below, teachers could ask the group for example words of the a_e, i_e, o_e, and u_e spellings to create a word wall. Students might then write a story, using as many silent final e words as possible.
Instructional Phonics Sequence
Generally speaking, all three phonics approaches follow a similar instructional order.
1. The most common sounds are introduced prior to the least common sounds.
- Short vowels and consonant sounds
- Ending consonant blends and “sh” and “th” voiced consonant digraphs
- Beginning consonant blends, “wh” and “tch” consonant digraphs, “sh” and “th” unvoiced consonant digraphs
- Long vowel sounds and silent final e
- Long vowel sounds and r-controlled vowels
- Diphthongs
2. Order of instruction separates letters that are visually similar e.g., p and b, m and n, v and w, u and n.
3. Order of instruction separates sounds that are similar e.g., /k/ and /g/, /u/ and /o/, /t/ and /d/, /e/ and /i/.
4. The most commonly used letters are introduced prior to the least commonly used letters.
5. Short words with fewer phonemes are introduced prior to longer words with more phonemes.
6. Continuous sounds e.g., /a/, /m/, are introduced prior to stop sounds e.g., /t/ because the continuous sounds are easier to blend.Check out Pennington Publishing’s Instructional Phonics Sequence with sound-by-sound spelling blending:
Get the Instructional Phonics Sequence FREE Resource:

Get the Animal Sound-Spelling Cards FREE Resource:

*****
My take? Synthetic phonics is the most efficient means of teaching the alphabetic code and should be taught systematically as part of any beginning reading program or reading intervention program. However, good reading and spelling programs provide additional analytic phonics activities, such as syllabication and spelling pattern word sorts. Plus, while most students learn with a synthetic approach, others respond best with an analytic approach. Good teachers also use incidental embedded phonics instruction as teachable moments to study words in depth as they use shared and guided reading. The best means of determining whether any method of reading instruction is working? Assessment. Flexible teachers use data to inform instruction and the instructional approach to meet the needs of individual students.
Get the Diagnostic Reading and Spelling Assessments FREE Resource:


The Science of Reading Intervention Program
The Science of Reading Intervention Program: Word Recognition includes explicit, scripted instruction and practice with the 5 Daily Google Slide Activities every reading intervention student needs: 1. Phonemic Awareness and Morphology 2. Blending, Segmenting, and Spelling 3. Sounds and Spellings (including handwriting) 4. Heart Words Practice 5. Sam and Friends Phonics Books (decodables). Plus, digital and printable sound wall cards and speech articulation songs. Print versions are available for all activities. First Half of the Year Program (55 minutes-per-day, 18 weeks)
The Science of Reading Intervention Program: Language Comprehension resources are designed for students who have completed the word recognition program or have demonstrated basic mastery of the alphabetic code and can read with some degree of fluency. The program features the 5 Weekly Language Comprehension Activities: 1. Background Knowledge Mentor Texts 2. Academic Language, Greek and Latin Morphology, Figures of Speech, Connotations, Multiple Meaning Words 3. Syntax in Reading 4. Reading Comprehension Strategies 5. Literacy Knowledge (Narrative and Expository). Second Half of the Year Program (30 minutes-per-day, 18 weeks)
The Science of Reading Intervention Program: Assessment-based Instruction provides diagnostically-based “second chance” instructional resources. The program includes 13 comprehensive assessments and matching instructional resources to fill in the yet-to-be-mastered gaps in phonemic awareness, alphabetic awareness, phonics, fluency (with YouTube modeled readings), Heart Words and Phonics Games, spelling patterns, grammar, usage, and mechanics, syllabication and morphology, executive function shills. Second Half of the Year Program (25 minutes-per-day, 18 weeks)
The Science of Reading Intervention Program BUNDLE includes all 3 program components for the comprehensive, state-of-the-art (and science) grades 4-adult full-year program. Scripted, easy-to-teach, no prep, no need for time-consuming (albeit valuable) LETRS training or O-G certification… Learn as you teach and get results NOW for your students. Print to speech with plenty of speech to print instructional components.
Grammar/Mechanics
analogy phonics, analytic phonics, decodables, embedded phonics, phonics appraches, phonics programs, Phonics Wars, reading curriculum, reading intervention program, reading wars, remedial reading program, research-based reading program, response to intervention, RTI, synthetic phonics, types of phonics

















