The Weekly Spelling Test

Spelling Lists and Tests
I often hear that weekly (or biweekly) spelling lists and tests with the traditional pretest-study-posttest methodology are “not supported by research” or are not “best practice.” Some teachers go so far to say that spelling lists and tests are “harmful.”
However, three renowned spelling experts seem to support this traditional methodology (citations follow at end of article).
Dr. Louis Moats: “Word lists organized by a concept or pattern of orthography; Test-study… then test on Friday… with immediate corrective feedback.”
Dr. Richard Gentry: “In every weekly unit, students take a pretest on the very first day. They find out what words they need to learn, focus on studying these unknown words, and take a Friday test to find out if they have mastered the unknown words. Our research based test-study-test cycle is an example of self-testing, which the study by Dunlosky and colleagues found to be the single most effective learning technique.”
Dr. Steve Graham: (In response to “What about the weekly spelling test?”) “If you have a spelling list that emphasizes, say like two or three patterns that you’re building off of through word sorts and learning, then you can learn about the underlying orthography, how letters and sounds are connected in English and that serves as a springboard for recognizing those kinds of patterns in words. We’ve got a meta-analysis of about 200 studies, and it would support that, as well. If you break your spelling list into the patterns that are emphasized and that’s what the focus of your spelling instruction is–not just the memorization of words, it can make a difference.”
Now these researchers would agree that at the K-2 levels, spelling should be taught in conjunction with explicit, systematic phonics and writing and not as a separate program. However, at 3rd grade and older, effective spelling instruction morphs (pun intended) into multi-syllabic encoding, advanced conventional spelling rules, spelling irregularities, Greek and Latin morphemes, and more. Additionally, intermediate and upper elementary, as well as middle school teachers will attest to the fact that many of their students still lack foundational spelling rules.
So, particularly for grades 3-8 students, how can we adapt the research-based pretest-study-posttest methodology to teach advanced spelling skills, while remediating any K-2 spelling patterns that students have not yet mastered? Can we use this methodology to differentiate spelling instruction and help older students keep up while they catch-up with efficient and easily-managed procedures and resources? Yes!
Follow the four-step weekly procedure used in my Differentiated Spelling Instruction grades 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 American and Canadian English spelling programs, and use the free resources.
1. Pretest: On the first day of each week, students take out a piece of binder paper for the spelling pretest. Dictate 15–20 grade-level spelling pattern words in the traditional word-sentence-word format to all your students on the first day of each week. No random, topical lists of colors, names of the months, etc. Have students self-correct from teacher dictation of letters in syllable chunks, marking dots below the correct letters, and marking an “X” through the numbers of any spelling errors. Don’t rob your students of this learning activity by correcting the pretest yourself. Immediate, corrective feedback is strongly supported by research.
2. Personalize: Students complete their own Personal Spelling List in Elkonin Sound Boxes to connect sounds to spellings in the following order of priority:
Pretest Errors: Students copy up to six of their pretest spelling errors onto a Personal Spelling List.
Last Posttest Errors: Students add up to three spelling errors from last week’s spelling posttest.
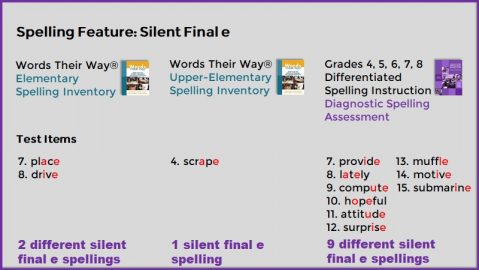
Diagnostic Spelling Assessment:
Administer the free Diagnostic Spelling Assessment to determine which previous grade-level spelling patterns your students have and have not mastered. Students add up to three unmastered spelling pattern words from this test.
Diagnostic American English Spelling Assessment: Print Assessment with “Normal speed” 22:38 and “Quick version 17:26 audio file links. Recording Matrix for Progress Monitoring
Diagnostic Canadian English Spelling Assessment: Print Assessment with “Normal speed” 18:53 and “Quick version 21:12 audio file links. Recording Matrix for Progress Monitoring
Writing Errors: Students add up to three teacher-corrected spelling errors found in student writing.
Supplemental Spelling Lists: Students select and use words from the following resources to complete their Personal Spelling List. You decide how many words should be included on the list.
- For remedial spellers:
Heart Words Heart Words Assessment
High Frequency Words (Organized by Spelling Patterns)
Most Often Misspelled Words
Commonly Confused Words - For grade level and accelerated spellers:
Greek and Latin Morphology (combined affixes and bases)
Academic Language—Tier 2 words previously introduced by the teacher Diagnostic Academic Language Assessments Grades 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8
3. Practice: Explain the spelling patterns, applicable spelling rules, and provide examples. Students complete spelling sorts to identify similarities and differences among the patterns. Add additional words which conform to the spelling patterns for practice; it’s the spelling pattern that students are practicing, not solely the words themselves.
Writing context clue sentences can also be helpful, especially with commonly confused words. Quick spelling review games aid study. Make sure to model how to study by saying the sounds as students write their corresponding letters. Deemphasize the visual approach to word memorization. No spelling shapes, rainbow writing, write the spelling word 10 times.
For remediation, students complete spelling pattern worksheets on spelling patterns not yet mastered (indicated by the Diagnostic Spelling Assessment). In my programs, each self-guided worksheet includes an explanation and examples of the spelling pattern, a comprehensive spelling sort, writing application, and a one-sentence formative assessment. Students self-correct the worksheet practice and the teacher grades the formative assessment. The recording matrices help teachers monitor progress.
4. Posttest: At the end of the week, or to save class time, at the end of two weeks, posttest on the Personal Spelling List. Note that a biweekly posttest covers two spelling pretests. Students take out a piece of binder paper and find a partner to exchange dictation of their Personal Spelling List words. Monitor the testing to ensure that students aren’t cheating. If using the biweekly posttest, consider telling students to test only the even (or odd) number words from their Personal Spelling List to save class time. The teacher grades the posttests.
Grades 3-8 Spelling Scope and Sequence (American and Canadian English Versions)
Many teachers want to create their own spelling lists, tests, and practice. To help grade-level teams do so, many teachers find this Grades 3-8 Spelling Scope and Sequence to be helpful. Both American and Canadian English Versions are included in this free download.
Get the Grades 3-8 Spelling Scope and Sequence FREE Resource:
![]()
Citations/Sources:
Here, Dr. Moats is quoting and citing Schlagal, B. (2001). Traditional, developmental, and structured language approaches to spelling: Review and recommendations, Annals of Dyslexia, 51, 147-176.
In “Current Research on Spelling Instruction,” Dr. Richard Gentry describes the key instructional procedures in his “Spelling Connections” series and cites the following researchers:
Dunlosky, J., Rawson, K.A., Marsh, E.J., Nathan, M.J., & Willingham, D.T. (2013). Improving students’ learning with effective learning techniques: Promising directions from cognitive and educational psychology. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 14(1), 4–58.
Dr. Gentry’s References at the end of the article include many supporting studies and meta-analyses https://www.zaner-bloser.com/products/pdfs/Current_Research_on_Spelling_Instruction.pdf Yes, all instruction is reductive. The spelling pretest-study-re-test procedure takes time away from other literacy learning.
On the 2-29-2024 Pedagogy Non-Grata podcast, teacher-researcher Nate Joseph asks noted writing expert, Dr. Steve Graham, the following: “Should I still do my weekly spelling test?”