
Differentiated Spelling Instruction Grades 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8
Despite having spelling instruction relegated to a mere editing skill tagged onto the end of the Writing Process by some writing “gurus,” good teachers continue to teach spelling through direct and differentiated instruction. Recent reading and writing research have reinforced the need to teach the structural components of words. Word analysis promotes spelling accuracy, correct pronunciation, and vocabulary development.
Spelling instruction is not solely the responsibility of primary elementary teachers. Intermediate, middle, and high school teachers need to both remediate spelling deficiencies and teach advanced spelling skills to their students. After learning the sound-spelling relationships, advanced spelling skills are acquired by learning and practicing the advanced spelling rules, syllabication and accent rules, and language derivations.
Following are articles, free resources (including reading assessments), and teaching tips regarding how to differentiate spelling instruction in the intermediate, middle, and high school from the Pennington Publishing Blog. Bookmark and visit us often. Also, check out the quality instructional programs and resources offered by Pennington Publishing. Both American English and Canadian English versions.
Diagnostic Spelling Assessments
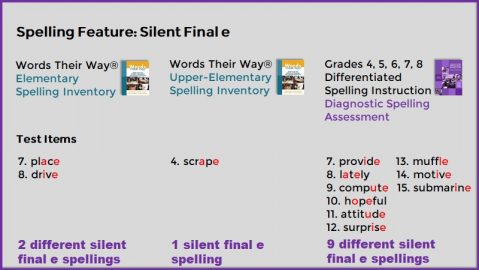
The 102 American English and 106 item Canadian English diagnostic assessments include the most common previous grade-level spelling patterns.
The test items are grouped by spelling patterns e.g., the four long /i/ spellings, to make posttest analysis simple. All spelling words are multi-syllabic to prevent students from identifying the words by “sight spellings” and to require recognition of the sound-spelling patterns within the context of syllables.
Assessment Formats
Choose the Diagnostic Spelling Assessment format which best suits your needs:
1. Paper Only: Teacher dictates the number of test items assigned to the grade levels, following the written administrative protocol. Students take the test on binder paper. Teacher corrects assessments according to directions and records spelling deficits on the Spelling Patterns Assessment Mastery Matrix.
Resources: Diagnostic Spelling Assessment teacher administration form; Spelling Patterns Assessment Mastery Matrix.
2. Audio and Paper: Teacher plays the 22:32 “slow speed” Diagnostic Spelling Assessment audio file for grades 4, 5, and 6 students or the 17:26 “fast speed” Diagnostic Spelling Assessment audio file for grades 7 and 8 students. The audio file includes all administrative directions. Students take the test on binder paper. Teacher corrects assessments according to directions and records spelling deficits on the Spelling Patterns Assessment Mastery Matrix.
Resources: Diagnostic Spelling Assessment 22:38 audio file; Diagnostic Spelling Assessment 17:26 audio file; Spelling Patterns Assessment Matrix.
3. Google Forms: Teacher shares either the Diagnostic Spelling Assessment Google Form with the 22:32 “slow speed” for grades 4, 5, and 6 students or the form with the “fast speed” for grades 7 and 8 students. Note that incorrect spellings with be accompanied by the Google red squiggly line indicating a spelling error. Students may be tempted to right click the word and select the correct spelling; however, if the teacher tells the students the purpose of the test and directs them not to self-correct, students will generally follow instructions. Telling students that they will receive the same amount of credit whether the spelling is accurate or not, and using the “fast speed” audio also helps students avoid the temptation of cheating. Teacher uploads the students’ Google Forms into the Spelling Patterns Assessment Mastery Matrix Google Sheets.
Resources: Resources: Diagnostic Spelling Assessment Google Forms with the 22:32 “slow speed” audio file for grades 4, 5, and 6 students or the the 17:26 “fast speed” audio file for grades 7 and 8 students; Spelling Patterns Assessment Mastery Matrix Google Sheets.
Spelling Scope and Sequence
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/spelling-scope-and-sequence/
Educators who once thought that spelling word check would solve students’ spelling and writing issues are squarely facing the fact that they do have a responsibility to teach spelling patterns. A spelling program with a comprehensive instructional scope and sequence, aligned to the Common Core Language Standards, College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards, and/or State Standards provides a well-defined instructional order. Check out the Common Core aligned grades 4-8 spelling scope and sequence of spelling patterns instruction.
Research-Based Spelling Worksheets
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/research-based-spelling-worksheets/
Of course spelling, grammar, usage, mechanics, and vocabulary scores plummeted during the late 1980s and early 1990s, sparking yet another “Back to Basics” movement. Mom had warned her son about the cyclical nature of educational movements and philosophies. The educational research provides insight as to what makes a spelling worksheet an effective instructional strategy for knowledge and/or skills acquisition.
Spelling Diagnostic Assessment
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/reading/how-to-teach-spelling-part-i/
This diagnostic assessment tests all of the important vowel sound-spellings that students should have mastered (but frequently have not) as foundations to conventional English spelling. Included is a convenient recording matrix for the teacher to plan differentiated instruction to remediate unmastered spelling patterns.
Middle School Spelling
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/middle-school-spelling/
Middle school students need advanced spelling instruction. What type? How to Teach?
Six Simple Steps to Teach Spelling
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/six-simple-steps-to-teaching-spelling/
Most veteran grades 4-8 teachers still teach spelling, especially in terms of spelling patterns, conventional spelling rules, derivational and etymological influences, accent placements and vowel shifts because they know how structural word analysis facilitates proper use of our language, better reading comprehension, and improved writing.
30 Spelling Questions, Answers and Resources
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/reading/30-spelling-questions-answers-and-resources/
In the midst of the 1980s whole language movement, California State Superintendent of Schools Bill Honig strongly encouraged principals to confiscate spelling workbooks from their teachers. Even today, spelling instruction remains a contentious topic. No other literacy skill seems to run the complete gamut of instructional implementation from emphasis to de-emphasis. The article includes the 30 spelling questions, answers, and resources to help teachers get a handle on what does and what does not work in spelling instruction.
Spelling Assessment Questions and Answers
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/spelling-assessment-questions-and-answers/
That said, as an author of numerous spelling programs and an often-used Diagnostic Spelling Assessment, I get two questions quite frequently: 1. Does a diagnostic spelling assessment make sense? and 2. How can we use the weekly pretest as a diagnostic assessment? But I’ll let teachers ask those questions in their own words…
How to Evaluate Spelling Programs
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/how-to-evaluate-spelling-programs/
With increasing attention on following Response to Intervention (RTI) guidelines, it makes sense to follow the criteria that orthographic research has established for quality spelling programs.
Ten Components of a Successful Spelling Program
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/ten-components-of-a-successful-spelling-program/
Teachers truly want to differentiate spelling instruction, but the materials, testing, instruction, and management can prove overwhelming to even the most conscientious professional. Using this Spelling Program Checklist can help teachers re-focus to improve their spelling instruction.
How to Differentiate Spelling Instruction
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/how-to-differentiate-spelling-and-vocabulary-instruction/
It makes sense to teach spelling and vocabulary together. Simply put, one affects the other. However, not all of our students are at the same levels of spelling and vocabulary mastery. So, how can an informed teacher (that is you) differentiate spelling and vocabulary instruction in an efficient manner?
Common Core Spelling Standards
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/common-core-spelling-standards/
The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) in English Language Arts provide instructional challenges for all conscientious upper elementary and middle school teachers. In addition to the Reading, Writing, Speaking & Listening Strands, teachers are expected to teach the grammar, mechanics, language application, spelling, and vocabulary Standards of the CCSS Language Strand (Standards L. 1-6). When establishing instructional priorities to address these Standards, many teachers have placed spelling (Standard L. 2) on the back-burner.
The “able” Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/the-able-or-ible-spelling-rule/
The “able” suffix spelling is often misspelled, even by very accomplished spellers. Here are the applicable spelling rules for the “able” suffix.
The Vulgar “a” Spelling
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/the-vulgar-a-spelling/
This lesson on the vulgar “a” includes definitions, examples, writing hints, practice, a formative assessment, writing application, and related CCSS standards.
Visual Spelling Strategies
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/visual-spelling-strategies/
Spelling is primarily an auditory skill; however, when used as an appropriate instructional component of a comprehensive spelling program, visual spelling strategies, such as these “picture spellings” can make sense.
Why Spelling Is So Difficult
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/why-spelling-is-so-difficult/
This article explains why the English Spelling System is so difficult to master. Seven suggestions give hope to even the most challenged speller to improve his or her spelling.
Top Twelve Spelling Trends and Fads
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/spelling-instructional-trends-and-fads/
A dozen of the most popular instructional spelling trends and fads over the last thirty years are described and rated as “TRUE” or “FALSE,” in terms of recent spelling research. Get ready to be challenged, and perhaps redirected in how you teach spelling.
Diagnostic Spelling Assessments
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=885&action=edit
In this series on How to Teach Spelling, this first post discusses and provides teaching resources for diagnostic spelling tests.
English Sound-Spellings
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/reading/how-to-teach-spelling-part-ii/
In this series on How to Teach Spelling, this second post discusses and provides teaching resources for teaching the sound-spelling system. The sound-spelling system is the foundation of conventional spelling.
Spelling Rules
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/how-to-teach-spelling-part-iii/
In this series on How to Teach Spelling, this third post discusses and provides teaching resources for teaching the eight conventional spelling rules. These eight rules go beyond the sound-spelling system to lead students to conventional spelling mastery.
The Plurals Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/the-plurals-spelling-rule/
The Plurals Spelling Rule Spelling Rule is one of the most consistent and useful spelling rules.
The Ending “ion” Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/the-ending-“ion”-spelling-rule/
The Ending “ion” Spelling Rule Spelling Rule is one of the most consistent and useful spelling rules.
The Ending “an” or “en” Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/the-ending-an-or-en-spelling-rule/
The Ending “an” or “en” Spelling Rule is one of the most consistent and useful spelling rules.
The Double the Consonant Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/the-double-the-consonant-spelling-rule/
The Double the Consonant Spelling Rule is one of the most consistent and useful spelling rules.
The Silent e Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/the-silent-e-spelling-rule/
The Silent Final e Spelling Rule is one of the most consistent and useful spelling rules.
The Final y Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/the-final-y-spelling-rule/
The Final y Spelling Rule is one of the most consistent and useful spelling rules.
The i before e Spelling Rule
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/grammar_mechanics/the-i-before-e-spelling-rule/
Although only 50% of English spellings conform to a predictable sound-spelling relationship, applying The i before e Spelling Rule will significantly increase spelling accuracy.
Spelling Lists and Tests
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/how-to-teach-spelling-part-iv/
Teachers who are serious about effective spelling instruction use the spelling pre-test as a diagnostic assessment to differentiate instruction. In this article, teachers will learn how to supplement the spelling pre-test with useful free hyperlinked resources.
Effective Spelling Practice
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/how-to-teach-spelling-part-v/
Effective spelling practice is not exclusively memorization. Good spelling practice connects to language development, vocabulary, structural analysis, auditory processing, and writing. Learn how to practice spelling effectively.
Vowel Team Spelling Games
https://blog.penningtonpublishing.com/spelling_vocabulary/vowel-team-spelling-games/
Spellers often struggle in the “Within Word” stage of spelling development. The key challenge for spellers within this spelling stage involves the vowel sound-spellings. These three spelling games will help your remedial spellers both recognize and practice these vowel team spellings.
More Articles, Free Resources, and Teaching Tips from the Pennington Publishing Blog
 English-Language Arts and Reading Intervention Articles and Resources
English-Language Arts and Reading Intervention Articles and Resources
Bookmark and check back often for new articles and free ELA/reading resources from Pennington Publishing.
*****
Pennington Publishing’s mission is to provide the finest in assessment-based ELA and reading intervention resources for grades 4‒high school teachers. Mark Pennington is the author of many printable and digital programs. Please check out Pennington Publishing for assessment-based resources created for teachers by a fellow teacher.
Grammar/Mechanics, Literacy Centers, Spelling/Vocabulary, Study Skills, Writing
differentiated spelling instruction, English spelling, Mark Pennington, orthography, spelling, spelling instruction, spelling lists, spelling rules, spelling word lists, structural analysis, teaching spelling, Teaching the Language Strand, word analysis, word parts, word study, Words Their Way








 As an MA Reading Specialist and author of quite a few spelling curricula (eight at last count), I’m often asked about spelling word lists by grade levels.
As an MA Reading Specialist and author of quite a few spelling curricula (eight at last count), I’m often asked about spelling word lists by grade levels. 





