Syntax in Reading and Writing

Syntax in Reading and Writing
The greatest bang for the buck for fluent readers to improve academic reading comprehension and writing sophistication? Syntax
What does the research say about syntax?
“In addition to lexical development, syntactic development plays a key role in reading comprehension” (Poulsen and Gravgaard, 2016 as cited in researchgate).
“Inadequate ability to process the syntax of language results in the inability to understand what is heard, as well as what is read. Beyond word knowledge, it is the single most powerful deterrent to listening and reading comprehension” (J.F. Greene, 2011).
“Fostering young writers’ awareness of the linguistic choices available to them in writing and how those choices differently shape meaning is developing their metalinguistic knowledge of writing” (Myhill, Jones, Lines, Watson as cited in Research Online).
Students will learn to understand (read) and apply (write) the key syntactic features in 18 weekly lessons of about an hour each. Focus is on function at the sentence level, not on rote memorization or drill and kill. Huge indebtedness to the late William Van Cleave… However, whereas William gave us the Why? and How? of reciprocal reading and writing syntactic instruction, this program gives you and your students the What?
But, how should we teach syntax?
The research over the last half-century is clear that isolated explicit grammar instruction is ineffective. However, the late William Van Cleave was certainly correct that implicit grammar instruction in the context of reading and writing provides no overarching framework, no consistent language of instruction, and not enough practice for students when taught only as problems arise. Bottom line? Neither explicit, nor implicit grammar camps link reading and writing instruction. As Van Cleave has concluded: “We need a new camp.”
That new camp is function-based syntax in reading and writing at the sentence level.
Syntax in Reading and Writing will help your students learn the function of syntactic tools in reading and writing. No endless grammar identification and terminology worksheets; no DOL error correction; no mini-lessons; but lessons which teach how challenging sentences are constructed.
The program provides syntactic content and examples, short identification practice, 153 complicated syntactic sentences to analyze and revise with sentence kernels, sentence combination, sentence expansion, and more. Plus, short writing applications to practice each syntactic lesson focus in a variety of genre.
The 18 parts of speech, phrases, and clauses weekly lessons are leveled from basic (elementary) to advanced (middle school and high school) and feature 5 lesson components (10–15 minutes each):
- Learn It! (the syntactic content and examples)
- Identify It! (a short practice section)
- Explain It! (analysis of challenging sentences featuring the syntactic focus)
- Revise It! (kernel sentences, sentence expansion and combination)
- Create It! (Short writing application with the syntactic focus in different genre).
Additionally, the teacher and students Reinforce It! by searching class and independent reading texts for syntactically similar sentences to analyze and explain.
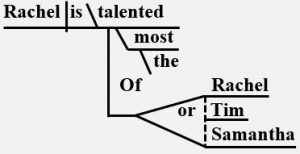
Check out the Syntax in Reading and Writing program. Pronoun Examples
*****

Pennington Publishing Grammar Programs
Teaching Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics (Grades 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and High School) are full-year, traditional, grade-level grammar, usage, and mechanics programs with plenty of remedial practice to help students catch up while they keep up with grade-level standards. Twice-per-week, 30-minute, no prep lessons in print or interactive Google slides with a fun secret agent theme. Simple sentence diagrams, mentor texts, video lessons, sentence dictations. Plenty of practice in the writing context. Includes biweekly tests and a final exam.
Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics Interactive Notebook (Grades 4‒8) is a full-year, no prep interactive notebook without all the mess. Twice-per-week, 30-minute, no prep grammar, usage, and mechanics lessons, formatted in Cornell Notes with cartoon response, writing application, 3D graphic organizers (easy cut and paste foldables), and great resource links. No need to create a teacher INB for student make-up work—it’s done for you! Plus, get remedial worksheets, biweekly tests, and a final exam.
Syntax in Reading and Writing is a function-based, sentence-level syntax program, designed to build reading comprehension and increase writing sophistication. The 18 parts of speech, phrases, and clauses lessons are each leveled from basic (elementary) to advanced (middle and high school) and feature 5 lesson components (10–15 minutes each): 1. Learn It! 2. Identify It! 3. Explain It! (analysis of challenging sentences) 4. Revise It! (kernel sentences, sentence expansion, syntactic manipulation) 5. Create It! (Short writing application with the syntactic focus in different genre).
Get the Diagnostic Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics Assessments, Matrix, and Final Exam FREE Resource:
![]()